Immagine
To boost your training, the Master's degree programme in Electronic Engineering is divided into innovative specialist tracks.
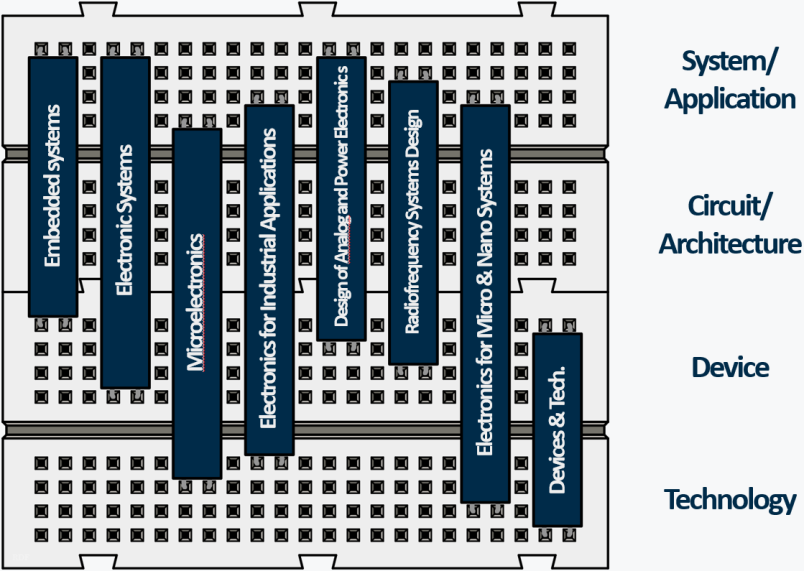
The guidelines give an overview from the point of view of the design level: in fact they cover the four design levels of an Electronic system in a different way, starting from the Technological aspect and moving towards Devices, Circuits and Architectures, up to at the System and Application level. The picture on the right gives an idea of which levels are covered by the various guidelines.
Immagine

Objective
- Ability to design a system where hardware and software must coexist and be optimized
Content
- Systems electronics and microelectronics
- Architectures: processors/FPGA
- Software: operating systems/drivers/algorithms
- Methods of HW/SW co-design and optimization
Immagine

Objective
- Project of complex systems (predominantly on-chip and on-board)
- Embedded, automotive, automation systems...
- Specifications, partitioning, synthesis and evaluation.
Content
- Microelectronic design and architecture (processors, FPGAs, system-on-chip)
- Project aid instruments, co-design
- Systems engineering
- Skills in Real-time Operating Systems
Immagine
Objective
- Design of complex integrated circuits/systems
- Digital and analog components
Content
- Integration technologies and integrated design
- Full custom and standard-cell Layout Design
- Architectural project
- CAD tools used in industry
Immagine

Objective
- Front-end between the physical world (analog) and (digital) information processing
- Back-end between numerical results and physical world (actuators - Mechatronics Industrial Automation)
Content
- Design of analog integrated circuits
- Components and power circuits
- Integrating A/D/power
Immagine

Objective
- To give students the skills to design electronics systems for industrial applications, with emphasis to robotics and automation
Content
- Photonics for industrial applications
- Architectures, networks and communication systems, either wired or wireless
- Design of advanced electronic drivers and AC/DC and DC/AC converters
- Power management, electromagnetic compatibility and engineering
Immagine

Objective
- To provide students with skills in the field of electronics systems for radio frequency and telecommunications
Content
- Analog electronics for high frequencies, from radio frequency to microwaves and millimeter waves
- High speed AD/DA conversion
- Wireless and wireline communication
- Computer Aided Design techniques for the design of high frequency circuits
Immagine
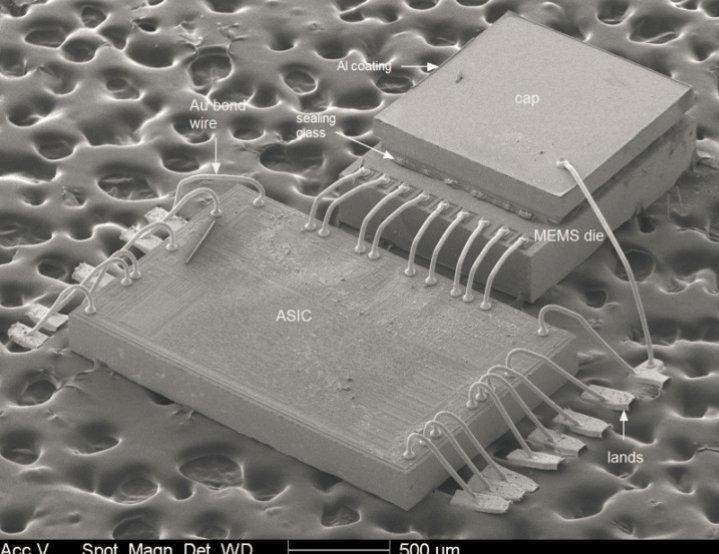
Objective
- Electronic technologies and micro / nano technologies for sensors and biomedicine
- Micro and Nano Integrated Systems
Content
- Technological and modelling bases (not only in Electronics but also Mechanics, Optics, Chemistry, Biology and Medicine)
- Construction of a complete system, from micro / nano systems to management of interfaces with the outside.
Immagine
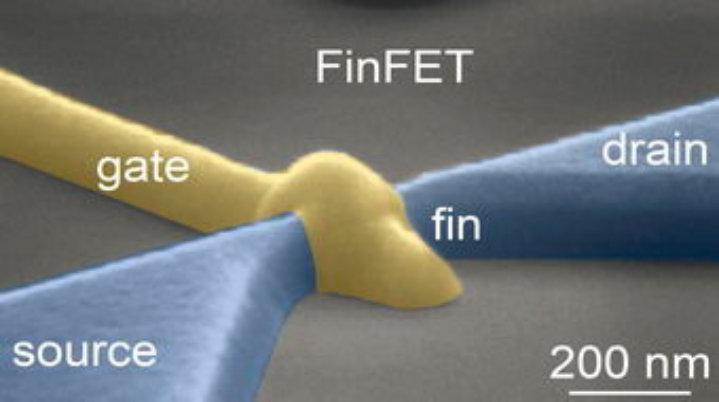
Objective
- Electronic technology and microtechnology
- different application sectors (radio, optical, transducers, sensors, ...)
Content
- Modelling and technology of devices and structures (semiconductors, organic or polymer materials)
- Electrical, thermal and structural characterization
- Technologic CAD
- micromachining techniques