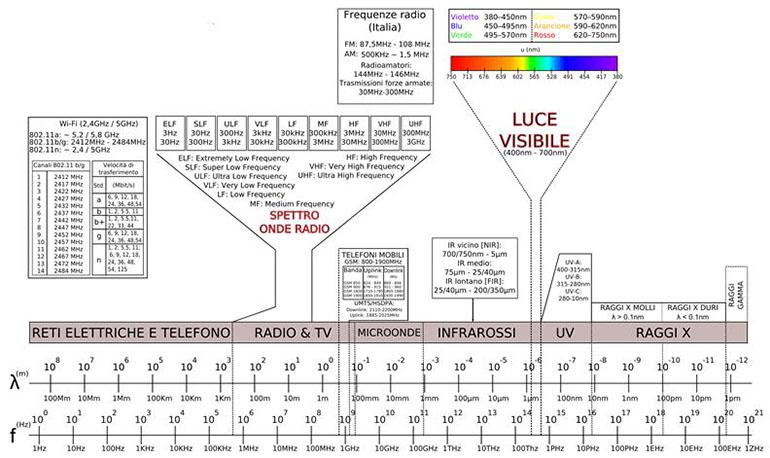
Electromagnetic spectrum radiations with energy less than 12 eV (characteristic of the range between UVC and X-rays) are non-ionizing radiations, as they have such a low amount of energy that when they react with biological tissues, they are unable to ionize ('break' the bond between the nucleus and electrons) the atoms of human tissues.
The range of ionizing radiations includes X-rays (characterized by a frequency in the range: 10^16 Hz - 10^19 Hz) and gamma rays (characterized by a frequency of 10^19 Hz).